Income inequality is a critical issue in today’s global economy, and the Gini coefficient is one of the most important tools used to measure it. Developed by the Italian statistician Corrado Gini in 1912, this metric provides a clear, quantitative representation of the disparity in income distribution within a given population. Whether you’re an economist, a policymaker, or simply someone interested in social justice, understanding the Gini coefficient can offer valuable insights into the dynamics of wealth distribution.
What is the Gini Coefficient?
The Gini coefficient, also known as the Gini index or Gini ratio, is a statistical measure that represents the extent of inequality within a distribution. While it is most commonly applied to income or wealth distributions, it can also be used to assess other types of data, such as health outcomes or educational attainment.
The Gini coefficient ranges from 0 to 1, where:
- 0 represents perfect equality: everyone has the same income.
- 1 represents perfect inequality: one individual has all the income, and everyone else has none.
In practice, no country has a Gini coefficient of 0 or 1; instead, most fall somewhere between these extremes, indicating varying levels of income inequality.
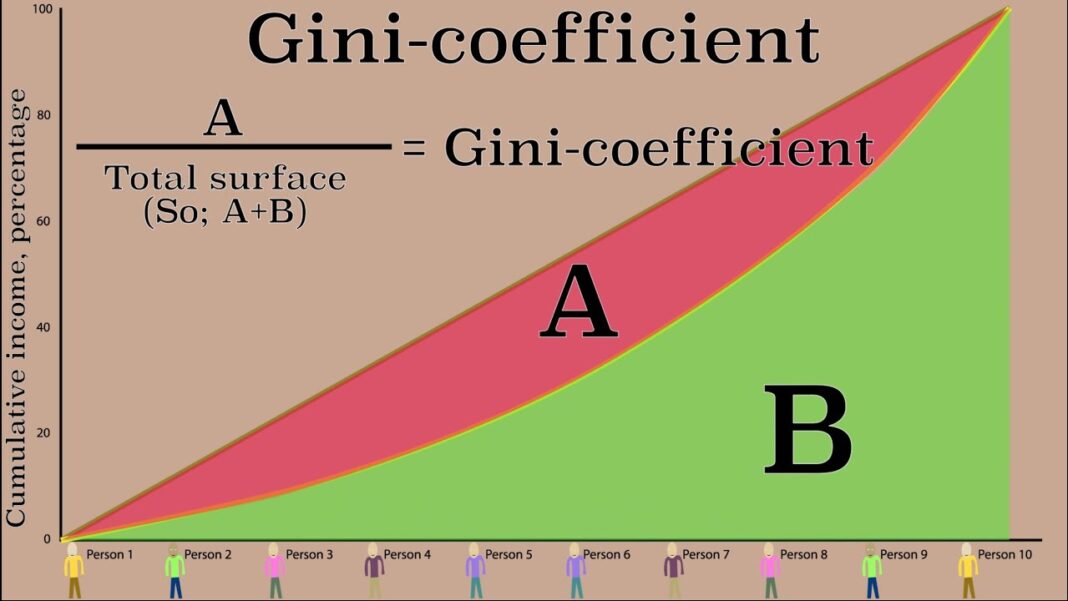
The Lorenz Curve: A Visual Representation
To calculate the Gini coefficient, the Lorenz curve is used. This curve graphically represents the distribution of income or wealth within a population. The x-axis of the Lorenz curve shows the cumulative percentage of the population, while the y-axis shows the cumulative percentage of income or wealth.
In an ideal scenario of perfect equality, the Lorenz curve would be a straight 45-degree line from the origin, known as the line of equality. However, in reality, the Lorenz curve bows below this line, with the degree of bowing indicating the level of inequality.
The Gini coefficient is calculated by measuring the area between the Lorenz curve and the line of equality, relative to the total area under the line of equality. This relationship is expressed mathematically as:
G=AA+BG = \frac{A}{A + B}
Where:
- A is the area between the Lorenz curve and the line of equality.
- B is the area under the Lorenz curve.
The larger the area A, the greater the income inequality, and hence, the higher the Gini coefficient.
How to Calculate the Gini Coefficient
Theoretical Calculation
The theoretical approach to calculating the Gini coefficient involves continuous data, usually represented in a functional form. This method is generally applied in academic or theoretical studies where income distributions are assumed to follow specific probability distributions.
Empirical Calculation
In most practical scenarios, the Gini coefficient is calculated using empirical data. This involves using a finite set of income data points, sorted from the lowest to the highest. The Lorenz curve is then plotted based on this ordered data, and the Gini coefficient is derived from the resulting curve.
Using a Gini Coefficient Calculator
For those who need a quick and accurate measure of income inequality, a Gini coefficient calculator can be an invaluable tool. These calculators are designed to handle raw data inputs, such as individual or household incomes, and automatically compute the Gini coefficient.
Steps to Use the Calculator:
- Input Data: Enter a set of incomes separated by commas, spaces, or line breaks.
- Calculate: Click the “Calculate” button.
- Interpret Results: The calculator will display the Gini coefficient and generate the Lorenz curve, allowing for a visual interpretation of income distribution.
These tools simplify the complex process of Gini coefficient calculation, making it accessible to a broader audience, including educators, students, and researchers.
Practical Applications of the Gini Coefficient
Global Income Inequality
The Gini coefficient is widely used by international organizations such as the World Bank, the United Nations, and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to assess and compare income inequality across different countries and regions. For example, Scandinavian countries typically have low Gini coefficients, reflecting their relatively equal income distributions. In contrast, many developing countries in Latin America and Africa have higher Gini coefficients, indicating significant income inequality.
Policy Implications
Governments and policymakers use the Gini coefficient as a key indicator to inform social and economic policies. By analyzing trends in the Gini coefficient over time, policymakers can assess the effectiveness of measures aimed at reducing income inequality, such as tax reforms, social welfare programs, and minimum wage laws.
For instance, the Gini coefficient for household income in the United States was 0.433 in 1992. By 2018, it had risen to 0.49, reflecting increasing income inequality. This upward trend has prompted debates about economic policies and the need for reforms to address wealth disparity.
Corporate and Market Analysis
Businesses and financial analysts also use the Gini coefficient to understand market conditions and consumer behavior. In regions with high income inequality, businesses might target products and services to specific income segments. Conversely, in areas with low inequality, products may be marketed more broadly.
Limitations and Considerations
While the Gini coefficient is a powerful tool for measuring inequality, it does have its limitations. For example, the Gini coefficient does not capture the source of income inequality or provide information about the underlying factors contributing to it. Additionally, it treats all income differences equally, regardless of whether they occur between the rich and the middle class or between the middle class and the poor.
Moreover, the Gini coefficient is sensitive to the distribution’s shape, which can lead to different interpretations in populations with similar Gini values but different income structures. Therefore, it is often used in conjunction with other measures of inequality to provide a more comprehensive analysis.
Conclusion
The Gini coefficient is an essential metric for understanding income inequality, offering a clear, quantifiable measure of how income is distributed within a population. Whether used by governments to shape policy, by international organizations to compare global income disparities, or by businesses to analyze market conditions, the Gini coefficient provides valuable insights into the economic health and social equity of societies.
By using tools like the Gini coefficient calculator, individuals and organizations can quickly assess income distribution and gain a deeper understanding of the inequalities that exist within different populations. As income inequality continues to be a pressing global issue, the Gini coefficient remains a crucial tool in the ongoing effort to create more equitable societies.